Scientific Review of Medium and Long Chain Fatty Acids
Medium-concatenation and Long-concatenation Fatty Acids Analysis Service
In biochemistry, a fatty acrid is defined as a long aliphatic concatenation with a carboxylic acrid functional group, either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids can be categorized into several groups according to the length of the chains: short-concatenation fatty acids (SCFA) with aliphatic tails of 2-six carbons; medium-chain fat acids (MCFA) with aliphatic tails of 6–12 carbons; long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) 13 to 21 carbons in aliphatic tails and Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) with aliphatic tails longer than 22 carbons. Fatty acids can also be divided into 2 groups according to whether they have double bonds between carbon atoms, unsaturated fat acids and saturated fatty acids. There are one or more double bonds between carbon atoms in unsaturated fatty acids, while saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen and have only unmarried bonds and without double bonds.
Essential fatty acids are divers as fatty acids required for biological processes that homo couldn't synthesize sufficient quantity from other substrates and must obtain from diet. Merely two fat acids, alpha-linolenic acrid and linoleic acid are considered as essential for homo beings, though some other fat acids like docosahexaenoic acrid and gamma-linolenic acid are classified as "conditionally essential because these fatty acids are essential under sure developmental or disease conditions. Those essential fatty acids are widely existed in animals and institute oils.
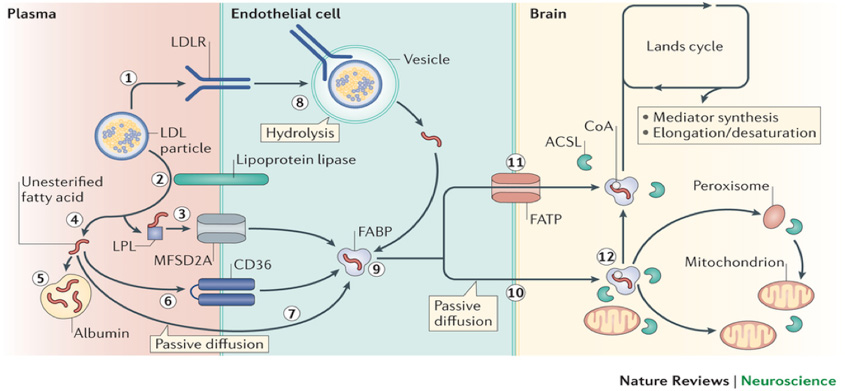
Well-nigh of the fat acids come from triglycerides or phospholipids. Fatty acids are of import sources of fuel in the trunk because they produce large quantities of ATP when metabolized in the body. Though nigh jail cell types tin can employ either glucose or fatty acids for energy generation, while long chain fatty acids can't transport the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and tin't exist used as energy source for central nervous arrangement. However, short-chain fat acids and medium-chain fatty acids can transport beyond the claret-encephalon bulwark (BBB) and enter the encephalon and act as an alternative energy source to ketone bodies.
Several analytical platforms are available to determine the concentration of FFAs in biological samples. Nonetheless, it is hard for most of the platforms to recover all fatty acids. Considering of their poor absorbance in visible-UV region and the absenteeism of appropriate chromophores or fluorescent groups, it is difficult to determine the concentration of fat acids by HPLC. Another procedures that are widely used are gas chromatography (GC) and GC-MS. GC-MS has been used for the quantitative analysis of carboxylic fatty acids for a long fourth dimension. The structural molecular ions generated from the MS detection source offer more than sensitive and reliable analysis of fatty acids present in lipid samples. Creative Proteomics has established sensitive, reliable, and accurate GC-MS method for quantification of medium-chain and long-chain fatty acids.
Platform
- GC-MS
Summary
- Identification and quantification of medium-chain and long-concatenation fatty acids by GC-MS.
Sample Requirement
- Normal Volume: 100ul plasma; 50mg tissue; 2e7 cells
- Minimal Book: 50uL plasma; 30mg tissue; 5e6 cells
Report
- A detailed technical report will exist provided at the end of the whole project, including the experiment process, GC-MS instrument parameters
- Analytes are reported as uM or ug/mg (tissue), and CV's are generally<ten%
- The name of the analytes, abbreviation, formula, molecular weight and CAS# would likewise be included in the study.
Medium-chain and Long-chain Fatty Acids Quantified in This Service
| Medium-chain and Long-concatenation Fatty Acids Quantified in This Service | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Butyric acid (C4:0) |
| two | Linoleic acid (C18:2n6c) |
| iii | Caproic acid (C6:0) |
| 4 | g-Linolenic acrid (C18:3n6) |
| 5 | Caprylic acid (C8:0) |
| 6 | Linolenic acid (C18:3n3) |
| 7 | Capric acid (C10:0) |
| 8 | Arachidic acid (C20:0) |
| nine | Undecanoic acid (C11:0) |
| x | cis-11-Eicosenoic acid (C20:1) |
| 11 | Lauric acid (C12:0) |
| 12 | cis-xi,14-Eicosadienoic acid (C20:2) |
| 13 | Tridecanoic acrid (C13:0) |
| xiv | cis-8,11,14-Eicosatrienoic acrid (C20:3n6) |
| 15 | Myristic acid (C14:0) |
| xvi | Arachidonic acrid (C20:4n6) |
| 17 | Myristoleic acid (C14:1) |
| 18 | Heneicosanoic acid (C21:0) |
| nineteen | Pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) |
| 20 | cis-11,14,17-Eicosatrienoic acid (C20:3n3) |
| 21 | cis-10-Pentadecenoic acid (C15:1) |
| 22 | cis-5,eight,11,fourteen,17-Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5n3) |
| 23 | Palmitic acid (C16:0) |
| 24 | Behenic acid (C22:0) |
| 25 | Palmitoleic acid (C16:one) |
| 26 | Erucic acid (C22:1n9) |
| 27 | Heptadecanoic acid (C17:0) |
| 28 | cis-thirteen,sixteen-Docosadienoic acid (C22:2) |
| 29 | cis-10-Heptadecenoic acid (C17:1) |
| 30 | Tricosanoic acid (C23:0) |
| 31 | Stearic acid (C18:0) |
| 32 | cis-iv,vii,x,13,sixteen,19-Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6n3) |
| 33 | Elaidic acid (C18:1n9t) |
| 34 | Lignoceric acid (C24:0) |
| 35 | Oleic acrid (C18:1n9c) |
| 36 | Nervonic acid (C24:1) |
| 37 | Linolelaidic acid (C18:2n6t) |
How to place an order: 
*If your organisation requires signing of a confidentiality agreement, please contact usa by email
With integrated set of separation, characterization, identification and quantification systems featured with excellent robustness & reproducibility, high and ultra-sensitivity, Creative Proteomics provides reliable, rapid and cost-constructive medium-chain and long-chain fat acids targeted lipidomics services.
* For Research Utilise Just. Not for utilise in diagnostic procedures.
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a calendar week. Enquiry
Online Research
Please submit a detailed description of your project. Nosotros volition provide you with a customized project program to meet your research requests. Yous tin can also send emails directly to for inquiries.
Source: https://www.creative-proteomics.com/services/medium-chain-and-long-chain-fatty-acids-analysis-service.htm
0 Response to "Scientific Review of Medium and Long Chain Fatty Acids"
Post a Comment